Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat joint problems. During arthroscopic surgery, a small camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the joint, providing the surgeon with real-time images. To enhance visibility and ensure a clear view of the joint, arthroscopy irrigation tubing plays a critical role. This tubing is used to deliver a sterile irrigation solution into the joint, flushing out debris, blood, and other fluids, ensuring that the surgical area remains clear during the procedure.
|
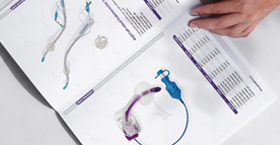
| GCMEDICA's Arthroscopy Irrigation Tubing |
1. Definition
Arthroscopy irrigation tubing is a specialized medical device that consists of a flexible tube used to deliver an irrigating fluid (usually saline or a sterile fluid) into the joint during an arthroscopic procedure. The irrigation fluid helps maintain a clear view of the surgical site by washing away debris, blood, and other materials that may obstruct the surgeon’s view or interfere with the procedure.
The tubing is typically connected to an irrigation system, which controls the flow rate and pressure of the fluid. In addition to aiding visualization, it can also help keep the joint distended, providing better access to the structures inside the joint.
2. Uses of Arthroscopy Irrigation Tubing
Arthroscopy irrigation tubing has several important uses in modern arthroscopic surgeries:
a) Clear Visualization of the Surgical Area
During an arthroscopic procedure, the surgeon needs a clear view of the joint to identify any issues such as cartilage damage, tears in ligaments, or bone irregularities. Irrigation tubing delivers a steady flow of sterile fluid that flushes out blood, debris, and other particles, ensuring the camera lens remains free of obstructions, providing a clear view throughout the surgery.
b) Joint Distension
In certain joint surgeries (such as knee, shoulder, or hip arthroscopy), distension of the joint is necessary for better access and to allow the surgeon to maneuver the arthroscope and instruments effectively. The fluid delivered through the irrigation tubing helps to expand the joint cavity, making it easier to perform procedures such as repairing torn ligaments, removing damaged tissue, or shaving down bone spurs.
c) Debris Removal
Surgical procedures often generate debris, including bone chips, tissue fragments, and other matter that may hinder the surgeon's ability to see or work effectively. The irrigation fluid flushes these materials out of the joint, helping the surgeon maintain a clean field of vision.
d) Cooling of Surgical Instruments
In some cases, the irrigation fluid can also help cool the surgical instruments used in the procedure. This is particularly important when thermal devices (e.g., radiofrequency probes) are used, as they can heat up during use and need to be kept at a safe temperature to prevent tissue damage.
e) Improvement of Tissue Healing
Some irrigation fluids are medicated or contain substances that promote healing. For example, certain solutions may be used to irrigate and clean the joint after a surgical repair, promoting the healing of the affected tissues and reducing the risk of infection.
3. Procedure Involving Arthroscopy Irrigation Tubing
The process of using arthroscopy irrigation tubing typically follows these general steps:
a) Preparation
Sterilization: The tubing and irrigation fluids are prepared under sterile conditions. The surgeon ensures that all components, including the irrigation system and fluid containers, are sterile to prevent infection.
Connection: The irrigation tubing is connected to the arthroscopic system and the sterile fluid reservoir, which contains the irrigation solution (usually saline). The opposite end of the tubing is attached to a port on the arthroscopic device, which is used to deliver the fluid into the joint.
b) Insertion of the Arthroscope
The surgeon makes a small incision to insert the arthroscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) into the joint. This incision is typically made near the joint of interest.
c) Irrigation Fluid Delivery
Once the arthroscope is inserted, the irrigation tubing is activated, and sterile fluid is delivered into the joint cavity through the tubing. The fluid washes over the surgical site, ensuring that any debris or blood is cleared away, and the joint remains distended for better visualization.
The surgeon may adjust the flow rate of the irrigation fluid based on the procedure’s needs. The amount of fluid used depends on the size of the joint and the complexity of the surgery.
d) Continuous Monitoring
The surgeon continuously monitors the effectiveness of the irrigation system, ensuring that the joint remains clear and the pressure is maintained at an optimal level to avoid injury to surrounding tissues. In some cases, the pressure may need to be adjusted based on the joint's condition or the procedure being performed.
e) End of Procedure
After the procedure is complete, the irrigation tubing is disconnected, and the joint is drained of excess fluid. The arthroscope and any instruments used are removed, and the incision is closed.
f) Post-Surgery
After the surgery, the patient is monitored for any complications, including infections or issues with fluid retention, as the irrigation process may introduce fluid into the joint that needs to be absorbed or drained.
4. Benefits of Arthroscopy Irrigation Tubing
Arthroscopy irrigation tubing provides several key benefits that make it an invaluable part of arthroscopic surgery:
a) Enhanced Surgical Precision
By ensuring that the surgical area remains clear, the irrigation system allows the surgeon to work with greater accuracy. This is crucial for avoiding damage to surrounding tissues and for performing intricate repairs within the joint.
b) Reduced Risk of Infection
Irrigation helps flush out bacteria and other harmful substances that may be present in the joint before, during, or after surgery. This reduces the risk of postoperative infection, which can complicate recovery and lead to further medical issues.
c) Minimized Tissue Damage
Since the joint is maintained at an optimal pressure and distension during the procedure, the surgeon can work in a more controlled environment, reducing the risk of inadvertently damaging sensitive tissues like ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
d) Improved Recovery
By keeping the joint clean and ensuring that only the necessary areas are exposed to the surgical instruments, the risk of complications is lowered, leading to a smoother recovery. Irrigation can also help to remove inflammatory cells or proteins that could hinder the healing process.
e) Better Visualization
The most immediate benefit of using irrigation tubing during arthroscopy is that it provides a clear view of the surgical site. By maintaining a clean field, the surgeon can better identify the source of pain or damage and make precise repairs.
f) Patient Comfort
Irrigation helps ensure a less invasive procedure, which can lead to reduced post-operative pain and faster recovery times. Minimizing the extent of damage to surrounding tissue helps reduce the risk of inflammation and discomfort post-surgery.
Conclusion
Arthroscopy irrigation tubing is an essential tool in modern arthroscopic surgery, providing vital assistance in ensuring clear visualization, joint distension, and the removal of debris. By maintaining a sterile, clean surgical environment, it helps surgeons perform delicate procedures with greater precision, reduces the risk of infection, and promotes faster recovery for patients. The role of irrigation tubing in arthroscopy underscores the importance of advanced technologies in improving patient outcomes and optimizing the efficacy of minimally invasive surgeries.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us